Parkinson's Disease
OVERVIEW
Parkinson’s disease is the second most common neurodegenerative disorder. It’s more prevalent among the elderly, but can affect people of all ages. Eminent British Physician James Parkinson was the first to describe this disease in the year 1817.In the last 200 years there has been tremendous progress in the field of Parkinson’s disease. Although majority of the patients in India are above 60 years of age in India, nearly 20 percentage of them are young onset and are below 40 years and rarely this disease might appear below 20 – 30 years.
There are several neurotransmitters in the brain and dopamine is one of the important neurotransmitter. Degeneration of dopamine secreting nerve cells in the substantia nigra of the brain leads to Parkinson’s disease. These symptoms appear after 50 – 60 parcent of the neurons are lost. Exact cause of the degeneration of these neurons is not clearly known. Sevaral researchers indicate repeated head injury, exposure to pesticides and drinking water from wells increase risk of Parkinson’s disease. 5 percent of them have other family members with Parkinson’s disease representing the genetic defects associated with it.
Clinical features & Symptoms :
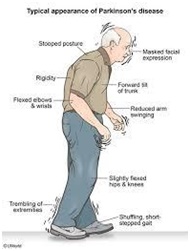
The main clinical features of this disease are slowness of activities of daily living, shaking of the hands, stiffness and imbalance. However, patients may not have all these together in the initial stages of the disease. These symptoms starts slowly and progress over time, hence people with any of the forementioned symptoms should visit a neurologist experienced in treating Parkinson’s disease (Movement disorder specialist).As this is a progressive disorder patients later develop all the fore mentioned symptoms including imbalance and falls, these symptoms are known as motor symptoms. They also develop several non-motor symptoms such as constipation, urinary problems, depression, psychosis, forgetfulness, easy fatiguability, sleep disturbances, poor smelling ability, loss of taste e.t.c. These non motor symptoms precedes the onset of motor symptoms and worsens a the disease progresses and results in significant morbidity.
Diagnosis:
Diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease is predominantly clinical but preferably MRI Brain is done to rule out other causes such as strokes, tumours etc. that mimick parkinson’s disease.Rare case may need radionuclide imaging Fluoro-Dopa positron emission tomography to clear ambiguity of diagnosis.
Management of Parkinson’s Disease:
The first line of management is usually through medication. Several medicines have been discovered in the past 4-5 decades. Levodopa is the cornerstone of management of Parkinson’s disease as it provides the greatest benefit to patients in terms of reduction of symptoms. The patients may have to take levodopa tablets 3-5 times in a day. Initially the affect of levodopa lasts for 4-5 hours , but as the disease progresses affectivity of levodopa wanes off and duration of action progressively decreases with appearance of side affects such as Dyskinesisas (Unwanted involuntary movements). In addition to levodopa other medications that are available are pramipexole, rasagline, trihexyphenidyl and amantadine. Patients of Young onset Parkinson’s disease are preferably started on pramipexole or ropinirole and other drugs are added based on requirement.
Deep Brain stimulation & Advanced Therapies :
Therapies for advanced Parkinson’s disease: After 4-5 years of medication Parkinson’s disease patients develop fluctuations which includes trouble some dyskinesias, off periods, non-motor fluctuations e.t.c. Options for these are tailored on individual patient basis which includes levodopa pump, apomorphine injections and deep brain stimulation surgery (DBS). Widely available therapy for advanced Parkinson’s disease is DBS procedure which works as a pace maker of the brain. DBS decreases the off periods, fluctuations , slowness, stiffness and rigidity in appropriately selected patient.
Future therapies and research is on closed loop DBS, disease modifying drugs and stem cell therapy is in the primordial stage.
Summary:
In a nutshell Parkinson’s disease is a progressive neurologic disorder that is treatable. Every patient requires a tailored individual approach. Many therapies are available based on the stage of the disease. In what ever stage the Parkinson’s disease may be a lot can be done to alleviate patient symptoms. Patient need to consult a neurologist specialised in movement disorders.






